Artificial Intelligence: Global M&A Update
Published January 17, 2019

Trends in AI
Our Principal & Managing Director, Patrick Ringland, contributed to the 2018 Q3 Global M&A Partners‘ Newsletter focused on Artificial Intelligence. Patrick leads Meridian Capital’s Technology Team. He has advised clients across an assortment of industry segments, including biotech, pharmaceutical, technology, media, and telecommunications. He has successfully advised Fortune 50 companies and privately held businesses and entrepreneurs on a variety of sell-side and buy-side, recapitalization, growth equity, and strategic advisory assignments
Introduction
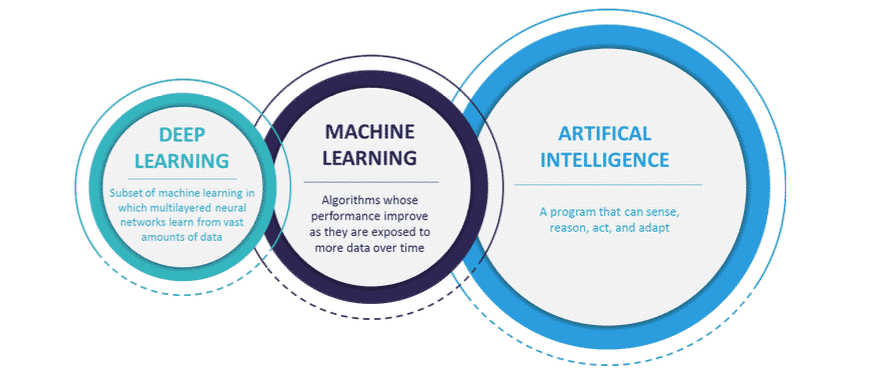
Artificial Intelligence (AI) could be the next force of digital disruption. It refers to systems or machines which can work or react like humans. AI includes multiple technologies, the most prominent among them are machine learning, deep learning and natural language processing (NLP). Early evidence points to the fact that AI can deliver real value to end users and can be a serious force of disruption. It is already being used across multiple industries including retail, healthcare, manufacturing, defence and education. It is anticipated that the impact of AI is likely to grow significantly over the next five years as it become more mature and easily deployable commercially.
There has been a spurt in the deal activity around companies with Artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. According to CB Insights, the number of acquisition of AI start-ups increased by 44% to 115 in 2017 from 80 in 2016 and has continued at a similar pace in 2018. According to the 2018 M&A trends report by Deloitte, technology acquisition is the no. 1 driver of M&A pursuits.
New AI technologies such as deep learning is surpassing the limits of previous machine learning. Though, machine learning has been attracting largest share of investment till now, it is likely that deep learning will take over going forward. Machine learning algorithms need to be trained by feeding large sets of data to them. This requires some form of human intervention and are therefore prone to human biases. However, deep learning, which uses artificial neural network to make decisions does not need any human training and are capable of learning on their own.
“Artificial Intelligence has fundamentally changed how we interact with the world. I believe its applications will continue to create huge opportunities for technology businesses on a global scale.”
Patrick Ringland, Principal & Managing Director
Meridian Capital